July 2024: a month of celebratory aerial art. It is time for a new sky?

July 4: In the United States, today marks Independence Day with festive sky illuminations over cityscapes from Alabama (“Thunder on the Mountain”) and Arizona (Scottsdale’s WestWorld) to Massachusetts with the Boston Pops on the city’s Esplanade playing the war-related “1812 Overture ” complete with cannon fire supplied by 101st Field Artillery accompanied by fireworks, and James Taylor at Tanglewood, all the way to Wyoming where Lander hosts a rodeo and celestial conflagration.

July 14: Bastille Day follows suit. Fireworks with the Eiffel Tower as background are a classic on this National Day. There a military parade on the Champs-Elysées. Some would observe that many national anthems celebrate war (can we celebrate peace?). Fireworks clog already-polluted urban air.

July 26: the Paris Olympics will feature 10,500 athletes floating along the Seine river in national team boats, with opening ceremony finale at the Trocadéro. Fireworks often illumine Olympic celebrations.
TIME FOR A NEW SKY?

But there are at least two public health reasons why fireworks should no longer be the light show of choice: urban pollution and risk of wildfires. And now, there is a technological opportunity to consider a new sky.
AIR POLLUTION

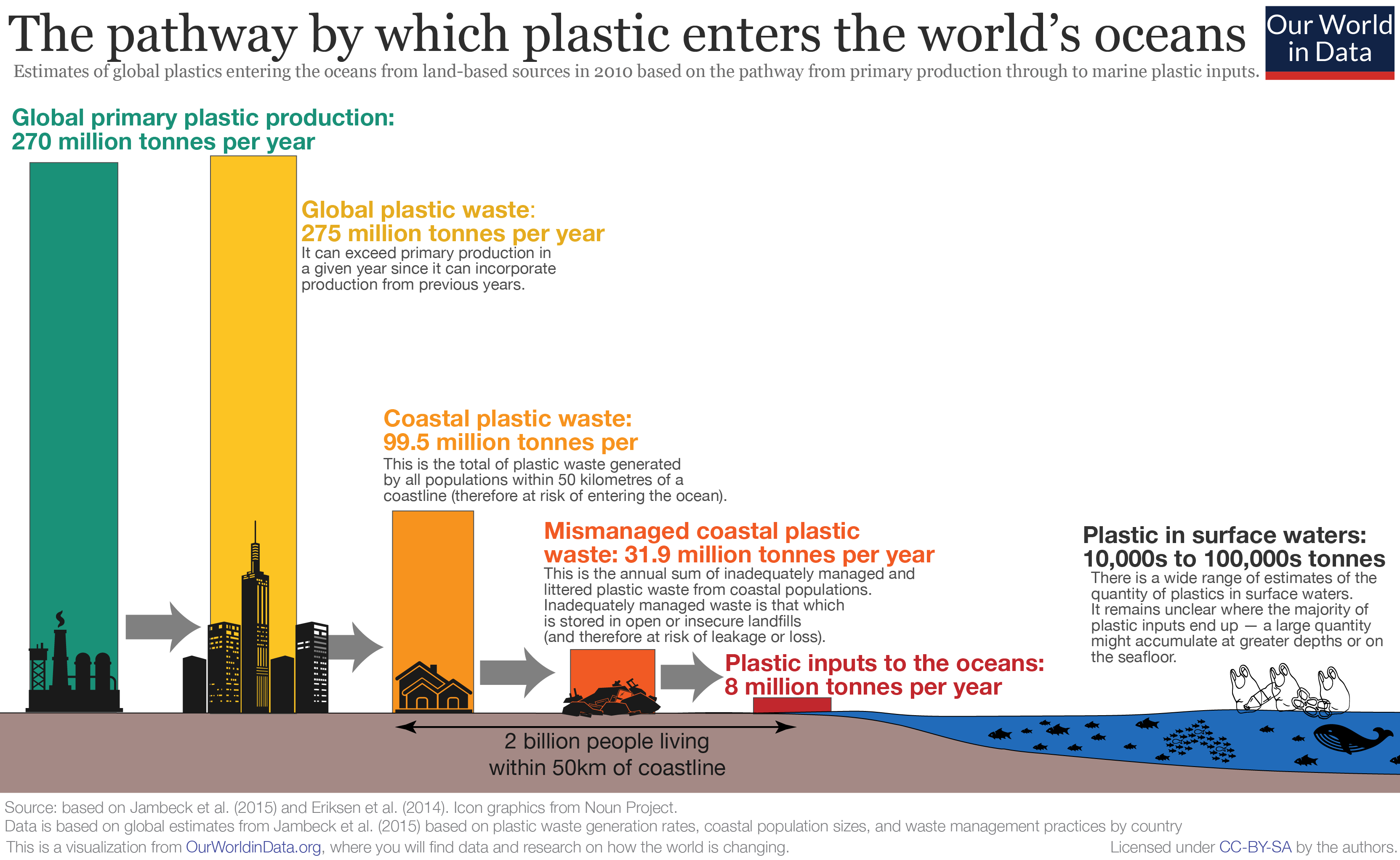
Air pollution and urban smog are a global problem. But this July, two places may have options for cleaner air. In the USA, many cities suffer air quality issues from ozone with Los Angeles, California the worst, followed by Phoenix, Arizona; Denver, Colorado; Houston, Texas; Las Vegas, Nevada; Chicago, Illinois; and Albuquerque, New Mexico having trouble (descending order). And then there is particulate pollution – deadly to lungs where tiny pieces lodge, causing chronic conditions and also deadly disease. From Bakersfield, Fresno, San Francisco/Oakland, and Los Angeles in California (highest) to Corpus Christi, Texas and Las Vegas, Nevada, the health of urban citizens is at risk.
Paris suffers air quality problems well above World Health Organization recommended limits. Levels of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and particulate matter have declined since France placed limits on diesel-fueled vehicles, but clouding the skies with explosions, however artistic, stresses the respiratory tracts of viewers, not to mention Earth’s atmosphere. Figures reveal that 7,900 premature deaths could have been avoided in Paris in 2022 if pollution were better controlled. What about 2024?
WILDFIRES

Climate change has brought increasing drought and with it, wildfires. In the United States, California is so prone to wildfires that the state established a tracking dashboard for residents to evaluate daily risk. So far, this summer has seen the Basin fire covering 13,980 acres (26% contained); the Bolt 3-2 fire damaging 10, 353 acres (98% contained). To date, 147,012 acres have burned: up 394%. The site also lists water shortages. Canada also suffered extensive wildfire damage in recent years (see above images from Sentinel-2A).
Did you know that wildfires peak around holidays when local folks set off their own fireworks at their house or area field? According to the US Forest Service, wildfires saw a predictable spike on July 4 during the period of 1992 to 2020. So-called “Roman candles” in Washington, DC burned down a 76-person residential building last week. In 2023, 9,700 people sought hospital emergency treatment for firework-linked injuries: half were children.
A NEW SKY

With threats of air pollution and wildfires, some cities are opting out of traditional fireworks and turning to drone sky art. Boulder, Colorado pivoted to drone shows after the Marshall Fire (2021/22) took two lives and 6,000 acres (2,428 hectares). California’s La Jolla and Ocean Beach opted for sky animations six years ago. Napa, a city known for festive toasts, will take precaution in the midst of a dangerous heat wave with attendant fire risks to present July 4th 2024 air choreography by 400 drones. In the UK, at the coronation of King Charles III, the light show was delivered by drones. At the recent Tokyo Olympics, drones ascended to offer sky art.
Drones are becoming a good investment: the market has grown from nil to $1 billion in 2021. Drone stocks are soaring – some as high as the new sky art we may see this July.
For a light show, by drone, click here.
American Lung Association. “State of the Air: Most Polluted Cities in 2024.” https://www.lung.org/research/sota/city-rankings/most-polluted-cities
Brooke, K. Lusk. “A New Sky.” 4 July 2023. Building the World Blog. https://blogs.umb.edu/buildingtheworld/2023/07/04/cities-wildfires-fireworks-and-a-new-sky/
Bogle, Jeff. “The Best Fireworks Displays in Every State.” 27 June 2024. Reader’s Digest.
Calmatters. “Track California Wildfires 2024.” https://calmatters.org/california-wildfire-map-tracker/
Kiszla, Cameron. “Fireworks can be breathtaking in more ways than one.” 3 July 2024. KTLA. https://ktla.com/news/local-news/fireworks-air-quality/
Maggiacomo, Taylor. “You don’t need your own fireworks to celebrate July 4.”4 July 2024. New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/live/2024/07’02/opinion/thepoint/you-dont-need-your-own-fireworks-to-celebrae-july-4
Napa, California. “Drone Show to Light Up Napa’s 4th of July Celebrations.” https://www.cityofnapa.org/CivicAlerts.aspx?AID=716.
RFI. “Paris air pollution still too high.” https://www.rfi.fr/en/france/20230413-paris-air-pollution-still-too-high-despite-slight-improvement
Tchaikovsky, Pyotr Ilyich. “1812 Overture – with Cannons” listen here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QUpuAvQQrC0
Williams, Ashley R. “Some US cities are replacing 4th of July fireworks with environmentally friendly drones.” 2 July 2023. CNN. https://www.cnn.com/2023/07/02/us/drones-replace-july-fourth-fireworks-trnd
Building the World Blog by Kathleen Lusk Brooke and Zoe G. Quinn is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 U