
Atmospheric rivers: 11. Snow: 55 feet (16.76 meters). Rainfall: thus far in 2023, more than all of 2022. Conservation mandates and restrictions: eased. Outdoor watering: again permitted. Reservoirs: many refilled. Is California’s drought officially over? Conditions are better, but concerns remain. The issues are not restricted to California, but the state serves as a case example.
GROUNDWATER – On the surface, things certainly look better. But California’s underground aquifers are still in trouble, some at lowest levels ever recorded. After previous droughts (2007-2009, 2012-2016), California’s groundwater in the agriculturally important Central Valley recovered only 34% (2007-2009 drought) to as little as 19% (2012-2016). During drought periods, groundwater supplied 60% of California’s water, so maintaining underground aquifers is critical.
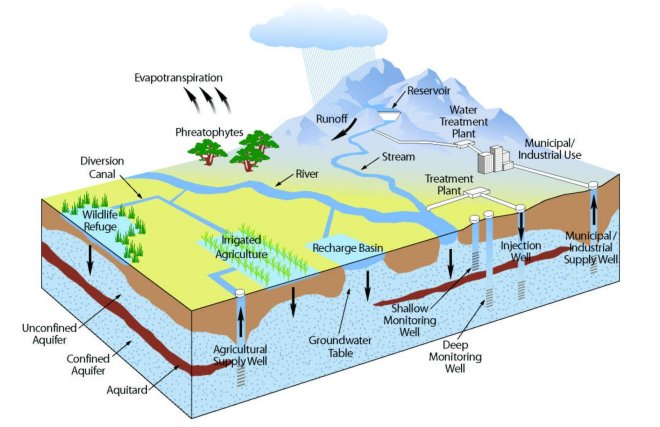
In irrigated agricultural regions with limited surface water supply, drought can have severe effects on groundwater. Recent innovations for storing floodwater underground in “water-capturing basins” hold promise. What kinds of future innovations will collect rain and flood water for future use? The Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA), passed in 2014, requires local agencies to form and fund groundwater sustainability agencies for high priority areas to control overuse of water by 2034. The United Nations raised awareness of the importance of groundwater by dedicating World Water Day 2022 to that resource with the motto: “Making the Invisible Visible.”

COLORADO RIVER – Surface water and underground aquifers are not the only sources. Water supplies from the Colorado River flow, at some distance, to cities and towns in Southern California. That river is still suffering through a two decade long drought that depleted reservoirs like Lake Powell and Lake Mead. Seven states, as well as many indigenous sovereign nations and also Mexico, share in the water according to rules set in the Colorado River Compact 0f 1922. If the seven states cannot come to agreement on water usage cutbacks, the federal government will step in. In April 2023, the U.S. Department of Interior’s Bureau of Reclamation introduced options.

FUTURE OF WATER– Satellite data confirm what we know all too well when 12 inches of rain in one day sweep through Ft. Lauderdale, Florida closing schools and highways, or floods drench Sindh Province, Pakistan,dislocating millions of people. We know and feel it when drought plagues land, dries up agricultural fields, drains reservoirs, and threatens hydroelectric facilities like those on the Po River of Italy, or Snowy Mountains Hydroelectric of Australia or Hoover Dam of the Colorado River in the United States.
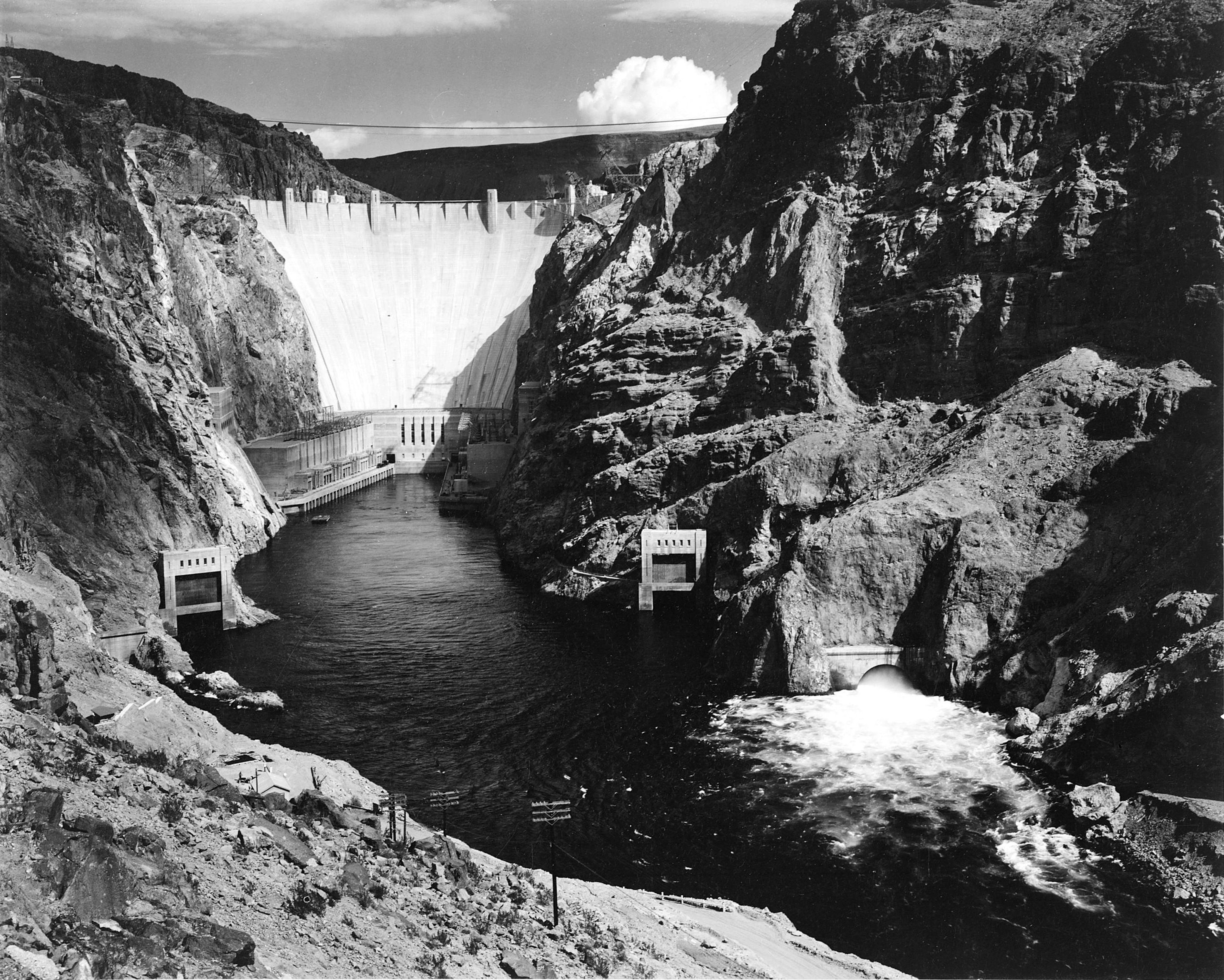

Hydroelectric power plants on rivers throughout the world are subject to changing water levels. If a river suffers drought, some hydroelectric facilities must be switched off. A recent study sounded the alarm. By 2050, 61% of all hydropower dams will be at high risk.

Climate change will make rains more intense and droughts more frequent. The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment satellite duo, known as GRACE and GRACE-FO will reveal a big picture in a long view. Dr. Matthew Rodell, Deputy Director for Hydrosphere, Biosphere, and Geophysics, Earth Sciences Division, NASA, and Dr. Bailing Li, of Goddard’s Hydrological Sciences Laboratory, led a team that studied over 1,000 weather events during the period 2002-2021. Rainfall extremes were noted in sub-Saharan Africa, North America, and Australia. Intense droughts were seen in South America, the United States, and elsewhere. Droughts outnumbered rain events by 10%. It’s costly: 20% of the USA’s annual economic loses were due to floods and droughts. Is there a solution? Using floodwater to recharge aquifers and irrigate agricultural land will be an area of innovation.

WATER FUTURES – Another development? Water Futures trading contracts such as the Veles California Water Index (NQH20) that launched on NASDAQ in 2018. Prices have fluctuated from below $300 per AF (acre-foot which equals 325,851 gallons or 1,233,480 liters) to 18 August 2022’s price of $1,134. At today’s post date, the price is $855. Is water a commodity or a right? Some say that commodity trading makes it possible for those who use quantities of water to plan, and plant, with more certainty.

WATER RIGHTS – But others might question water trading. On 28 July 2010, the United Nations General Assembly passed Resolution 64/292 that recognizes water and sanitation as a human right. In 2022, the Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights adopted General Comment No. 15, with Article 1.1 stating “The human right to water is indispensable for leading a life in human dignity. It is a prerequisite for the realization of other human rights.” Some would say that the right to sustainable, healthy water goes beyond human rights. New Zealand’s Whanganui River recently received personhood legal status, granting the river its own rights.

California Department of Water Resources. “Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA). Includes VIDEO.https://water.ca.gov/programs/groundwater-management/sgma-groundwater-management
Charles, Dan. “Water is scarce in California. But farmers have found ways to store it underground.” 5 October 2021. All Things Considered, NPR. Includes AUDIO. https://www.npr.org/2021/10/05/1037370430/water-is-scarce-in-california-but-farmers-have-found-ways-to-store-it-undergroun
Insights Editorial Team. “What Investors Should Know About Trading Water in the Futures Market.” 12 January 2021. Boston University. https://insights.bu.edu/what-investors-should-know-about-trading-water-in-the-futures-market
NASDAQ. “Nasdaq Veles California Water Index Fture (H20). https://www.nasdaq.com/market-activity/futures/h20
New Zealand. “Te Awa Tupua – Whanganui River Claims Settlement Act of 2017.” https://www.legislation.govt.nz/act/public/2017/0007/latest/whole.html
O’Malley, Isabella. “Scientists confirm global floods and droughts worsened by climate change.” 13 March 2023. PBS. https://www.pbs.org/newshour/science/scientists-confirm-global-floods-and-droughts-worsened-by-climate-change
Rodell, Matthew. and Bailing. Li. “Changing intensity of hydroclimatic extreme events revealed by GRACE and GRACE-FO.” Nature Water. 1 (3): 10.1038/s44221-023-00040-5 and https://www.nature.com/articles/s44221-023-00040-5
Rohde, Melissa M. “Floods and droughts are intensifying globally.” 13 March 2023. Nature Water 1, 226-227 (2023). https://www.nature.com/articles/s44221-023-00047-y
Sommer, Lauren. “3 reasons why California’s drought isn’t really over, despite all the rain.” 23 March 2023. Morning Edition, NPR. Includes AUDIO. https://www.npr.org/2023/03/23/1165378214/3-readons-why-californias-drought-isnt-really-over-despite-all-the-rain
United Nations. “Human Right to Water and Sanitation.” https://www.un.org/waterforlifedecade/human_right_to_water.shtml
Wada, Yoshihide., et al., “Global depletion of groundwater resources.” Geophysical Research Letters 37,1. https://agupubx.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2010GL044571 and https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL044571
Weir, Bill. “Thousands of acres are underwater in California, and the flood could triple in size this summer.” 15 April 2023. CNN. https://www.cnn.com/2023/04/15/us/tulare-lake-california-flood-climate/index.html
Building the World Blog by Kathleen Lusk Brooke and Zoe G. Quinn is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 U
