
Leonardo DiCaprio, Jennifer Lawrence, Meryl Streep, Cate Blanchett, Ariana Grande, Tyler Perry and others star in the science fiction noir comedy “Don’t Look Up” by Adam McKay. It’s an allegory about climate change, government, politics, and media. The film set a Netflix record for the most views in a single week: maybe you have seen this movie. If you are among those, like DiCaprio and others, who are concerned about climate change, you may wonder what you as an individual can do. NASA has an invitation for you. Do Look UP!

GLOBE CLOUD CHALLENGE welcomes citizen scientists to use the GLOBE Observer to identify clouds in their own area, timing observations with satellite flyovers. Satellites have a hard time identifying clouds, but these formations are easily seen from Earth. NASA hopes to collect 20,000 cloud observations.
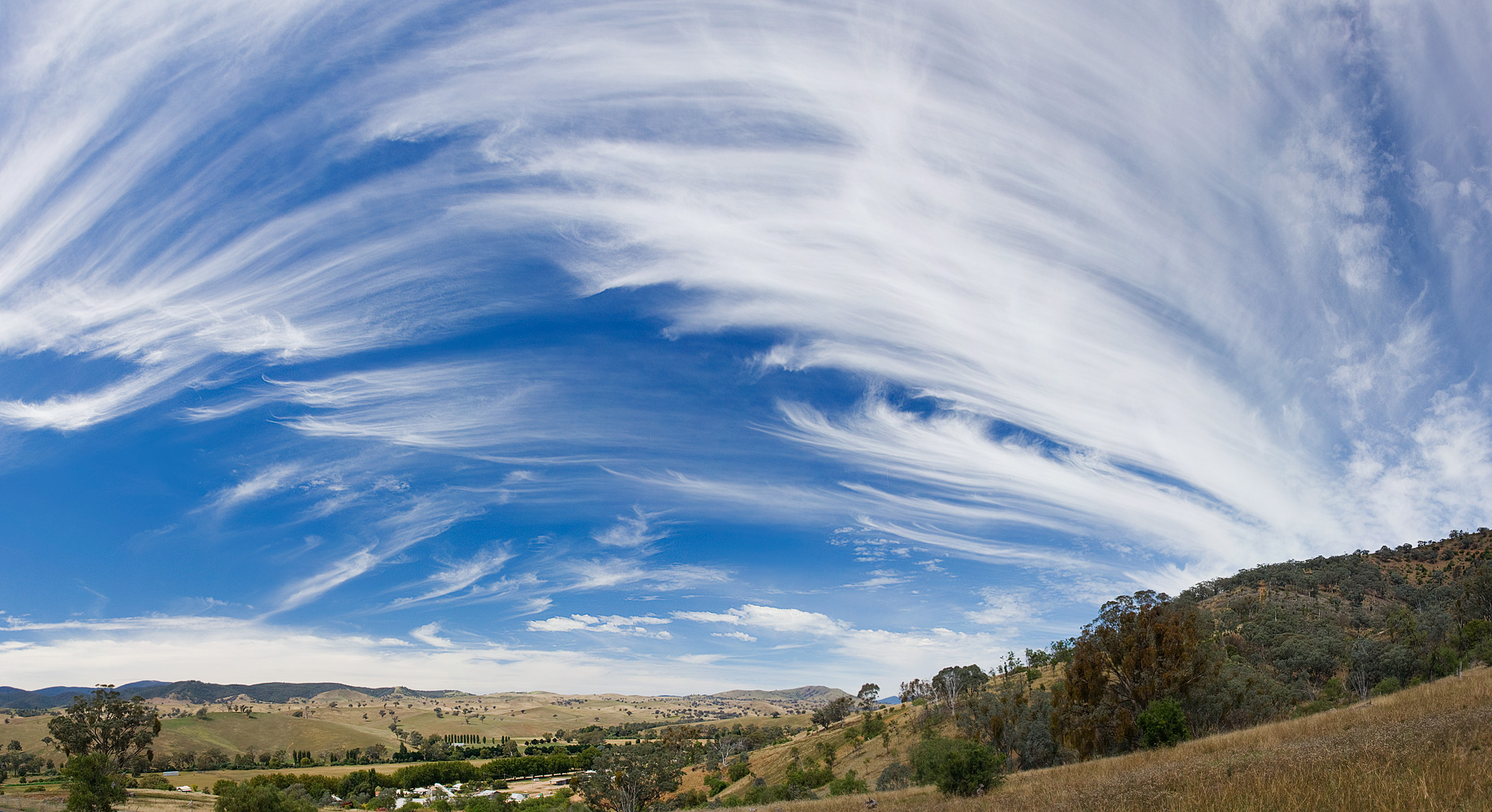

What are clouds and why do they appear? Formations of water vapor change into gas that condenses with dust or salt from sea spray to form liquid or ice: when the accumulation is sufficient, a cloud happens. Even if you’ve never flown through a cloud, you’ve probably walked through one: on land, the same process produces fog.

High, thin clouds let sunlight through yet still prevent heat from escaping to space via infrared radiation: there is a net warming result. Low, thick clouds reflect sunlight but have no impact of infrared radiation: there is a net cooling effect. Without clouds, we’d have a much warmer planet. With climate change and global warming, clouds are very much part of the solution.

NASA’s cloud-observation satellites include Aqua, Aura, Calipso, CloudSat, and Terra fly over the Earth. Soon, the data will be matched with NOAA’s GOES-T. Clouds are one of the aspects related to climate change. According to Marilé Colón Robles, lead atmospheric scientists for the Clouds team at Langley Research Center, “Each cloud affects Earth’s energy balance differently.” (NASA 2022)
Here’s how to participate. Download the GLOBE Observer APP (available to those in 120 GLOBE member countries. Register as an observer, and then go outside and look UP. The challenge runs until February 15, 2022. After that, keep the app active: as a citizen scientist, you can also use the app to observe and report on three other categories: mosquito habitat mapping, land cover, and trees. Here’s the link: https://apps.apple.com/us/app/globe-observer/id1090456751

If you are not able to go outside, you can still participate. With the NASA GLOBE CLOUD GAZE app, you can look at photos, identify cloud types, and tag via a Zooniverse online platform. Here’s that link: https:www.zooniverse.org/projects/nasaglobe/nasa-globe-cloud-gaze
NASA. “NASA GLOBE Cloud Challenge: 2022: Clouds in a Changing Climate.” 12 January 2022. https://www.nasa.gov/feature/langley/nasa-globe-cloud-challenge-2022-clouds-in-a-changing-climate
NOAA. “Clouds and Climate.” https://psl.noaa.gov/outreach/education/science/clouds_and_climate.html
Pearce, Fred. “Why clouds are the key to new troubling projections on warming.” 5 February 2020. Yale Environment 360. https://e360.yale.edu/features/why-clouds-are-the-key-to-new-troubling-projections-on-warming
Building the World Blog by Kathleen Lusk Brooke and Zoe G. Quinn is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Un
