
Can the orbital commons bring the world together? That was the vision of COMSAT. It all started with a 1955 article “Orbital Radio Relays” by John R. Pierce of Bell Labs, AT&T’s incubator for new ideas. Perhaps Pierce had read Arthur C. Clarke’s article “Extra-Terrestrial Relays,” published a decade before. When the first Trans-Atlantic Telephone Cable TAT-1 was laid in 1956 and Russia launched Sputnik in 1957, necessary pieces were in place. By 1960, AT&T applied to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for an experimental communications license. Two years later, the Communications Satellite Act presented a framework still relevant today. INTELSAT took the early leadership, achieving the first satellite-based global coverage on July 1, 1969. Just 19 days later, 500 million people around the world turned on televisions (the internet would come later) to witness, live, the first human setting foot on the moon.
Connectivity for All. But not everyone had a television, then; and not everyone has internet access now. Opening the World Wide Web to universal access, and enterprises like OneWeb, Starlink, and Project Kuiper, may finally achieve the goal of a global village.

OneWeb has reached a definitive milestone. OneWeb has now launched the final set of satellites needed to complete its array providing global connectivity for those who need it most. Founded in 2012 by Greg Wyler, OneWeb was acquired by the United Kingdom (UK) in March 2020 in a deal with UK government and Bharti Enterprises Ltd. On 26 March 2023, OneWeb’s launch by NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) positioned 36 new satellites, achieving desirable redundancy over the 588 needed for global coverage. Theme of the launch? “Hello world!”

Starlink, a division of SpaceX, also aims to offer connectivity “to anywhere, from anywhere.” Starlink began launching satellites in 2019, focusing on individual customers, especially those in rural locations. In contrast, OneWeb concentrates on businesses and commercial providers.

Project Kuiper, Amazon’s endeavor to place communications satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), shares the goal of global connectivity. Many places in the world do not have internet access needed for school, science, and communication. Janet Phan of Project Kuiper and founder of Thriving Elements, expands communications equality and opportunity with a commitment to bring more girls and women into STEM careers through mentoring. Project Kuiper’s satellite constellation will work with Amazon’s network of ground stations (Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS). Kuiper customers will install a home outdoor terminal intended to be affordable ($400) and lightweight (less than five pounds (2.27 kilograms); for more modest price-point customers, a smaller and less expensive terminal will provide basic connectivity. The chip driving it all – “Prometheus.”
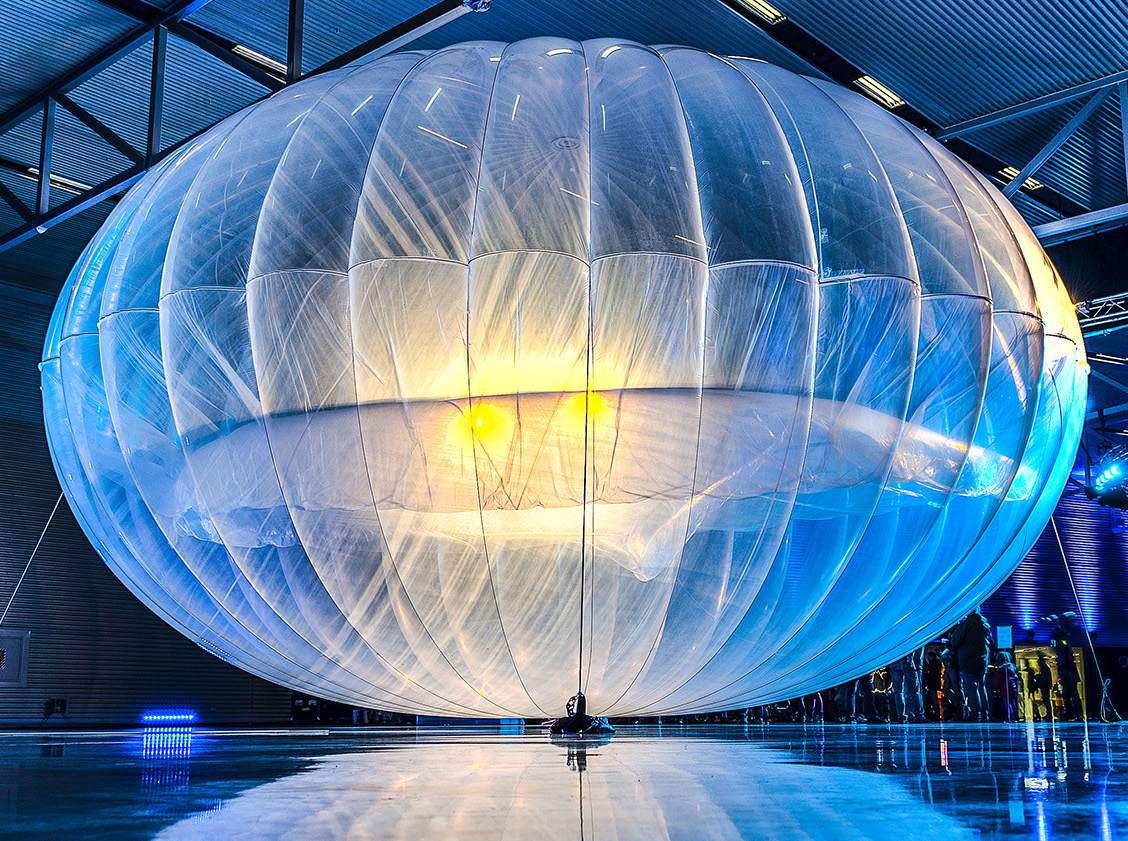

Project Loon was a promising vision that ran out of air. An Alphabet Inc. subsidiary, Loon LLC aimed to provide internet access to remote areas using high-altitude balloons to form an aerial wireless network. Hence the name: “Loon” as in “Balloon.” Started as an R&D project in 2011, Loon became a separate entity in 2018. Using National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) data to identify wind layers with the right speed, Loon would place balloons in a chain to allow signals to pass from orb to orb, connecting to an internet antenna attached to the side of a residential or commercial building. First experiments were in California and New Zealand. The next year, Loon tested in Brazil, and later in Sri Lanka. Loon’s unique advantage was demonstrated after Hurricane Maria hit Puerto Rico; Loon brought 100,000 people back online in the storm’s destructive aftermath. But commercial viability proved elusive and Project Loon closed on 21 January 2021. Loon’s legacy continues. Project Taara, a pan-African vision, harnesses some of Loon’s technology to extend connectivity with the use of light beam internet technology as a way to plug critical connectivity gaps in rural areas.
World Wide Web Foundation upholds the goal of “Establishing the open Web as a basic right and a public good.” With 160 partner organizations in 70 countries, the World Wide Web Foundation was launched in 2009 by Sir Tim Berners-Lee and Rosemary Leith. It has helped 600 million people access the web. Sir Tim Berners-Lee established the world wide web (that’s the “www” in an internet address) and gave it to the world for free. Global connectivity remains a challenge: almost half of the world still lacks internet access. You can help.

The global satellite market is expected to grow by 9% from 2023-2029, accelerated by advances in the internet of things (IoT) and increased capacity in wireless interconnection between terrestrial and space-based technology. It’s an attractive market because global internet traffic will grow over 20% – annually. But there are vast differences in connectivity, with 7x difference between fastest and slowest internet speeds. In addition to the above companies, contenders include SES, Viasat, Intelsat, Telesat, General Dynamics, Cobham Limited, Gilat Satellite Networks, EchoStar, Inmarsat, Eutelsat, Hughs Network Systems, Arqiva, Russian Satellite Communications Company, Thaicom, Globecast, Telespazio, and Telstra, according to the World Teleport Association.

It’s getting crowded up there, with so many satellites vying for optimal position. One concern is how to retrieve non-functional satellites before they become orbital debris. As of November 2022, the U.S. Space Surveillance Network found 5, 465 operating satellites in orbit. But these are among 25,857 objects circling the Earth. That tally only accounts for objects large enough to track. There are more than 128 million pieces of space debris smaller than 0.4 inches (1 centimeter). Even a tiny fleck can damage a satellite. There’s a tech term for such flecks: Micrometeoroid and Orbital Debris (MMOD).
Orbital justice: law and governance of space. A McKinsey report summarizes the challenges and opportunities for global governance of this shared frontier. The European Space Agency (ESA) introduced in 2022 the “Statement for a Responsible Space Sector” espousing principles of governance, inclusive social benefit, fair access to space, preservation of Earth through space-based monitoring, and promotion of human rights. Space, and the communications spectrum, belong equally to everyone on the Earth. How can you choose your internet provider with these principles in mind?
Amazon. “An Amazon employee explains how she’s helping bring more girls into STEM jobs.” 22 March 2023. Amazon. https://www.aboutamazon.com/news/workplace/an-amazon-employee-explains-how-shes-helping-bring-more-girls-into-stem-jobs
Amos, Jonathan. “OneWeb launch completes space internet project.” 26 March 2023. BBC Science & Environment. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-65066669
Clarke, Arthur C. “Extra-Terrestrial Relays.” October 1945. Wireless World, pages 305-8. Facsimile at http:www.lsi.usp.br/~rbianchi/clarke/ACC.ETR2.gif
Davenport, Justin. “OneWeb completes initial constellation with launch from India.” 25 March 2023, includes link to launch VIDEO. https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2023/03/oneweb-18/
Davidson, Frank P. and Kathleen Lusk Brooke. “COMSAT: The Communications Satellite” in Building the World, Volume II, pages 623-639. Greenwood: 2006. ISBN: 0313333742 and 9780313333743.
European Space Agency (ESA). “Statement for a Responsible Space Sector.”2022. https://www.esa.int/About_Us/Responsibility_Sustainability/Statement_for_a_Responsible_Space_Sector_Initiative
Gatto, Giacomo and Alyssa Goessler. “Can better governance help space lift off?” 22 February 2023. McKinsey. Includes AUDIO article. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/aerospace-and-defense/our-insights/can-better-governance-help-space-lift-off
Gehhardt, Chris. “U.K. government acquires OneWeb in curious move.” 3 July 2020. Nasa Space Flight (NSF). https://www.nasaspaceflight.com
Goguichvili, Sophie, et al., “The Global Legal Landscape of Space: Who Writes the Rules on the Final Frontier?” 1 October 2021. Wilson Center. https://www.wilsoncenter.org/article/global-legal-landscape-space-who-writes-rules-final-frontier
Imarc Group. “Top Players in the Satellite Communication (SATCOM) Market.” 29 November 2021. https://www.imarcgroup.com/satellite-communication-companies
Krisman, Victoria. “World Teleport Association Publishes Top Operator Rankings for 2021.” https://www.worldteleport.org/news/594359/World-Teleport-Association-Publishes-Top-Operator-Rankings-f0r-2021.htm
Pierce, John Robinson. The Beginnings of Satellite Communications. History of Technology Monograph. Berkeley, California: San Francisco Press, 1968. ISBN: 0911302050, and 9780911302059.
United Nations. Office of Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA). “United Nations Register of Objects Launched into Outer Space.” https://www.unoosa.org/oosa/en/spaceobjectregister/index.html
Whalen, David J. The Origins of Satellite Communications, 1945-1965. Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution Press, 2014. ISBN: 9781935623601
Building the World Blog by Kathleen Lusk Brooke and Zoe G. Quinn is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 U
