
Cities are known for fast food: the drive-through, the grab and go, the snack stop, pop-up restaurants, food trucks, street cafes and food stalls. Fast food can also be found on shelves of urban convenience and grocery stores. One of the world’s favorite quick treats is the instant noodle. In 2020, 116 billion servings of instant noodles were enjoyed. (Cairns 2022)
Singapore, a city created with trade and diversity as founding principles, is home to the launch of new kind of instant noodle – good for taste and for the environment, too. Based in Singapore, WhatIF Foods has introduced a noodle made from the Bambara Groundnut.
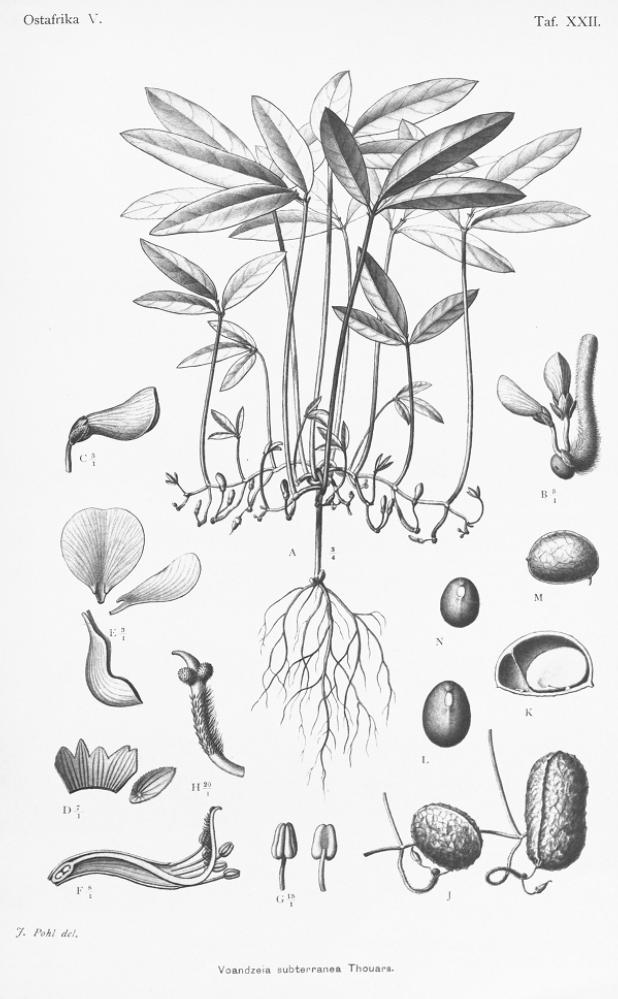
Bambara (Vigna subterranea) is in the legume family and grows underground (like peanuts): it originated in West Africa and is now grown across the world. It’s what is known, nutritionally, as a complete food: offering protein, carbohydrates, amino acids, minerals, vitamins, and fiber. WhatIF Foods produces “BamNut” flour made into noodles. The noodles are a bit pricier than the cheapest brands, but many people may value their superior nutrition.

Bambara Groundnut, or Vigna subterranea, currently comprises a very small part of food supply market (production in Africa is 0.3 million tons) versus the more traditional noodle dough made from wheat (776.6 million metric tons per year globally). But that may change – because Bambara is drought-tolerant. Many areas of the world already suffering drought (from states served by the Colorado River in the United States, to African and Australian areas experiencing drought and expecting more due to climate change and warming). Crops that can survive in dry soil will be in demand. Recent figures from the United Nations reveal that dry soil chokes 40% of agricultural land, and 56 acres (23 hectares) of arable land are lost to drought EVERY MINUTE.

There are 300,000 edible plant species, but just three (rice, maize, wheat) comprise 86% of all exports. According to Professor Victoria Jideani of Cape Peninsula University of Technology in South Africa, governments should subsidize agricultural diversity, such as the bambara groundnut, that can resist drought, support food security, and broaden the plant-based dietary options for a future-forward table. By 2050, 68% of the world’s people will live in cities. Land is limited, not only by population growth demands but also by agricultural needs. Optimal use of arable land will be one of the factors in balancing population, food security, and environment.

WhatIF Foods are currently sold in Singapore and produced in factories located in Australia and Malaysia, are sold in Asia, and in the regulatory approval process in the European Union. Privately financed, the company is now attracting investors. In the United States, you can purchase WhatIF products (noodles are just one of the products) online. Looking for instant noodle recipes? Here’s eight from eight countries.
Adetokunboh, Adeola, Anthony Obilana, Victoria Jideani. “Enzyme and Antioxidant Activities of Malted Bambara Groundnut as Affected by Steeping and Sprouting Time.” March 2022. Foods 11 (6): 783. DOI:10.3390/foods11060783
Cairns, Rebecca. “This Singaporean startup has reinvented the instant noodle.” 9 May 2022. CNN Business. https://www.cnn.com/2022/05/08/business/whatif-bamnut-sustainable-instant-noodles-climate-hnk-intl-spc/index.html
Cheetham, Peter and Christoph Langwallner, co-founders of WhatIF Foods. https://whatif-foods.com/
Jideani, Victoria. Cape Peninsula University of Technology, South Africa. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Victoria-Jideani
United Nations Environment Programme. “#FridayFact: Every minute, we lose 23 hectares of arable land worldwide to drought and desertification.” 12 February 2018. https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/story/fridayfact-every-minute-we-lose-23-hectares-arable-land-worldwide-drought
Building the World Blog by Kathleen Lusk Brooke and Zoe G. Quinn is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Un
