The year 2020 will go down in history for many reasons, including climate change. Temperatures were 1.08 degrees Fahrenheit (0.6 Celsius) warmer than the 1981-2010 average and 2.25 degrees Fahrenheit (1.25 Celsius) above pre-industrial times. Rising temperatures have consequences. In January of 2020, Australia suffered wildfires burning an area bigger than Florida. In summer, Atlantic hurricane season brought 30 named storms, carrying more water (warming oceans produce more water, higher waves, increased flooding). Western United States areas like California, Nevada, Oregon, Washington witnessed fires that destroyed 10.3 million acres. In the Arctic, data from the Copernicus Climate Change Service showed the region is warming faster than feared, more than twice the pace as the rest of the globe, with 5.4 degrees Fahrenheit (3 degrees Celsius). Environmental scientists noted that 2020 set a record for carbon dioxide concentrations, rising to 413 ppm (parts per million) in May of 2020, even with Covid-19 lockdowns. (Kann and Miller, 2021)
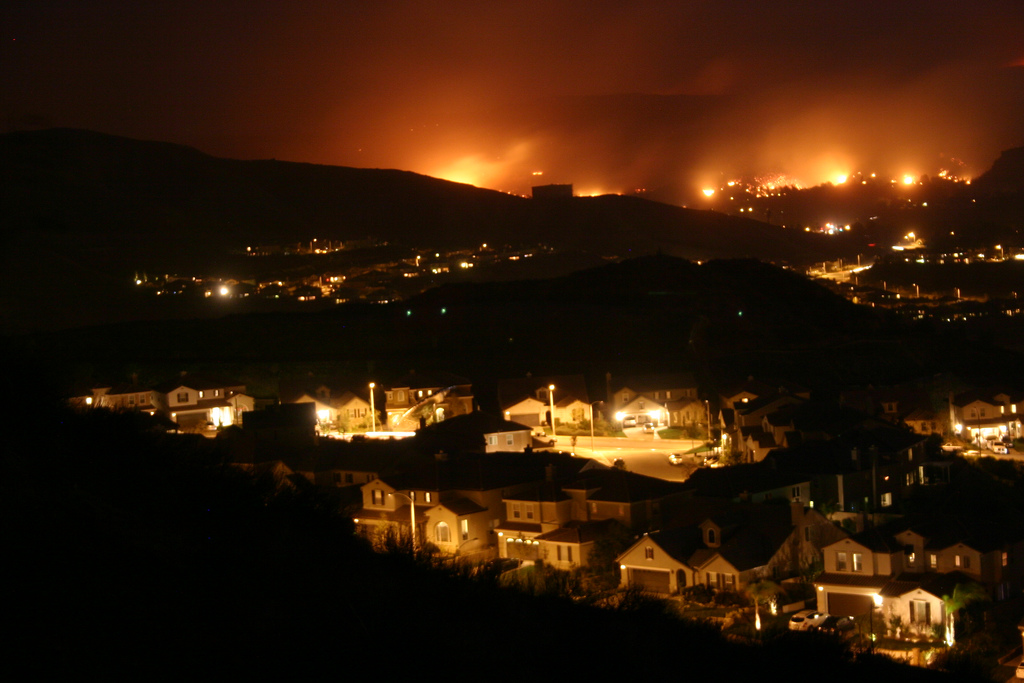 “Wildfire in Santa Clarita, California.” Image: wikimedia.
“Wildfire in Santa Clarita, California.” Image: wikimedia.
Price tag? $95 billion. And that’s just for U.S. climate-related damage, according to Munich Re, insurance company to other insurance firms that covered damage from Atlantic storms and California wildfires. Chief climate scientist of Munich Re Ernst Rauch warned that building in high-risk areas added to losses. Hurricanes were significant in damage, causing $43 billion in losses. Convective storms (like hailstorms and tornadoes) caused $40 billion. Wildfires added up to $7 billion including destruction of crops, endangering food security. Residential and business properties sustained damage and claimed insurance losses, over 4000 properties in Oregon and many more in California. According to Donald L. Griffin of American Property Casualty Insurance Association, “We can’t, as an industry, continue to just collect more and more money, and rebuild and rebuild and rebuild in the same way.” (Flavelle, 2021) Beyond the United States, the numbers are just as dire. Cyclone Amphan struck Bangladesh and India in May, resulting in $14 billion in damage. Asia sustained $67 billion in losses from natural disasters.
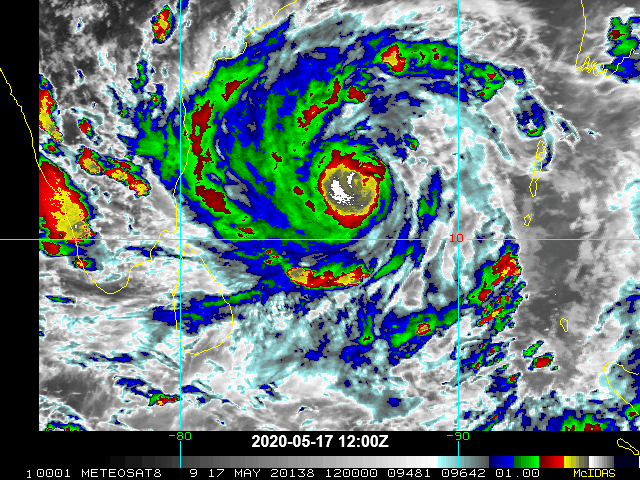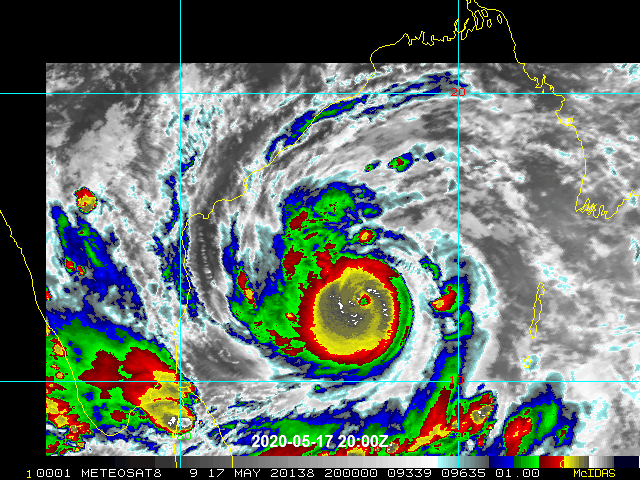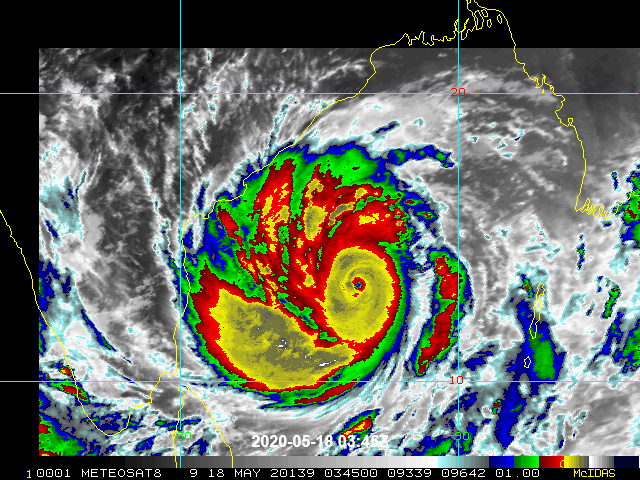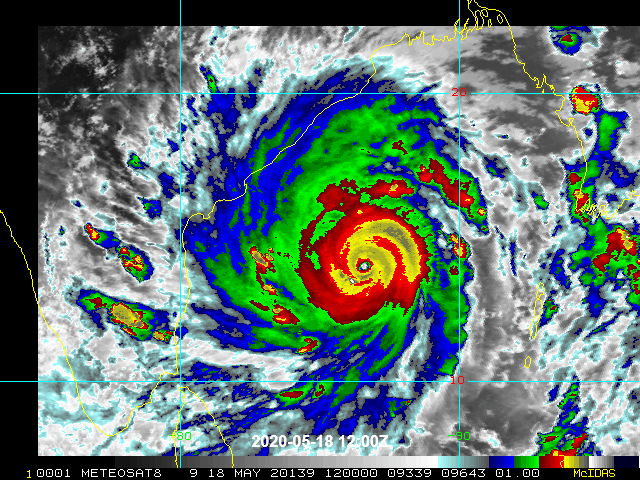 Cyclone Amphan May 2020. Image: wikimedia commons.
Cyclone Amphan May 2020. Image: wikimedia commons.
What does this mean for 2021? Following the money and perhaps led by the insurance industry, new ways to rebuild may lead us into the New Year. We’ll take a look at some hopeful trends, next.
American Property Casualty Insurance Association. https://www.apci.org
Flavelle, Christopher. “U.S. Disaster Costs Doubled in 2020, Reflecting Costs of Climate Change.” 7 January 2021. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/01/07/climate/2020-disaster-costs.html?referringSource=articleShare
Kann, Drew and Brandon Miller. “2020 was tied for the hottest year ever recorded — but the disasters field by climate change set it apart.” 8 January 2021. CNN.com. https://www.cnn.com/2021/01/08/weather/2020-global-temperatures-tied-for-warmest-on-record-copernicus/index.html
Munich Re. https://www.munichre.com/en.html
Thanks to Jason W. Lusk for editorial guidance and suggestions.
Building the World Blog by Kathleen Lusk Brooke and Zoe G. Quinn is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unp

