
“Lievre de l’astrologie chinoise,” by Alice-astro (image) and Miuki (character), 2013. Wikimedia CC3.0. Included with appreciation.
Welcome, Year of the Water Rabbit. Seasons may give us the year, but the moon tells us when the year is new. Amidst feasts and fireworks, this year’s water rabbit may also bring scientific good tidings. Did you know that Chinese tradition places a rabbit on the moon? And now that rabbit may have discovered lunar water.

“Chane’e, The Moon Goddess,” Late Yuan or early Ming Dynasty. Courtesy of Art Institute of Chicago, ARTIC artwork ID: 1108 23. Public Domain. Included with appreciation.
An ancient myth tells of Chang’e spirited from Earth to the Moon in a lovers’ tangled tale. She became the Moon goddess. But even a goddess can become lonely, so she was allowed to have a pet: a rabbit. Chang’e and her pet rabbit Yutu entered space lore when NASA’s Apollo 11 crew exchanged banter with Houston Mission Control just before the lunar landing in 1969, as the astronauts promised to look for the two lunar mythic figures. When China sent its first lunar probe to the moon in 2007, it was named Chang’e-1: its little robotic rover was name Yutu – Jade Rabbit. Chang’e was just getting started: in 2022, Chang’e-5 and its rover Yutu discovered evidence of water on the moon.

“Chang-e-5 orbiter ascender separation” by China News Service, 2020. Creative commons 4.0. Included with appreciation.
Water on the moon is a big discovery. Water is necessary for human habitation: carrying needed water into space would severely limit stays. Water could encourage space agriculture: one can consume, and carry, only so much tubular food. Finally, water – yielding hydrogen – might provide rocket fuel. Processing lunar water will be a technical challenge, but having water to start with is essential. Thanks to Chang’e – moon goddess – and Yutu, the Water Rabbit (among other space missions globally), human exploration may open wider, and longer, horizons.
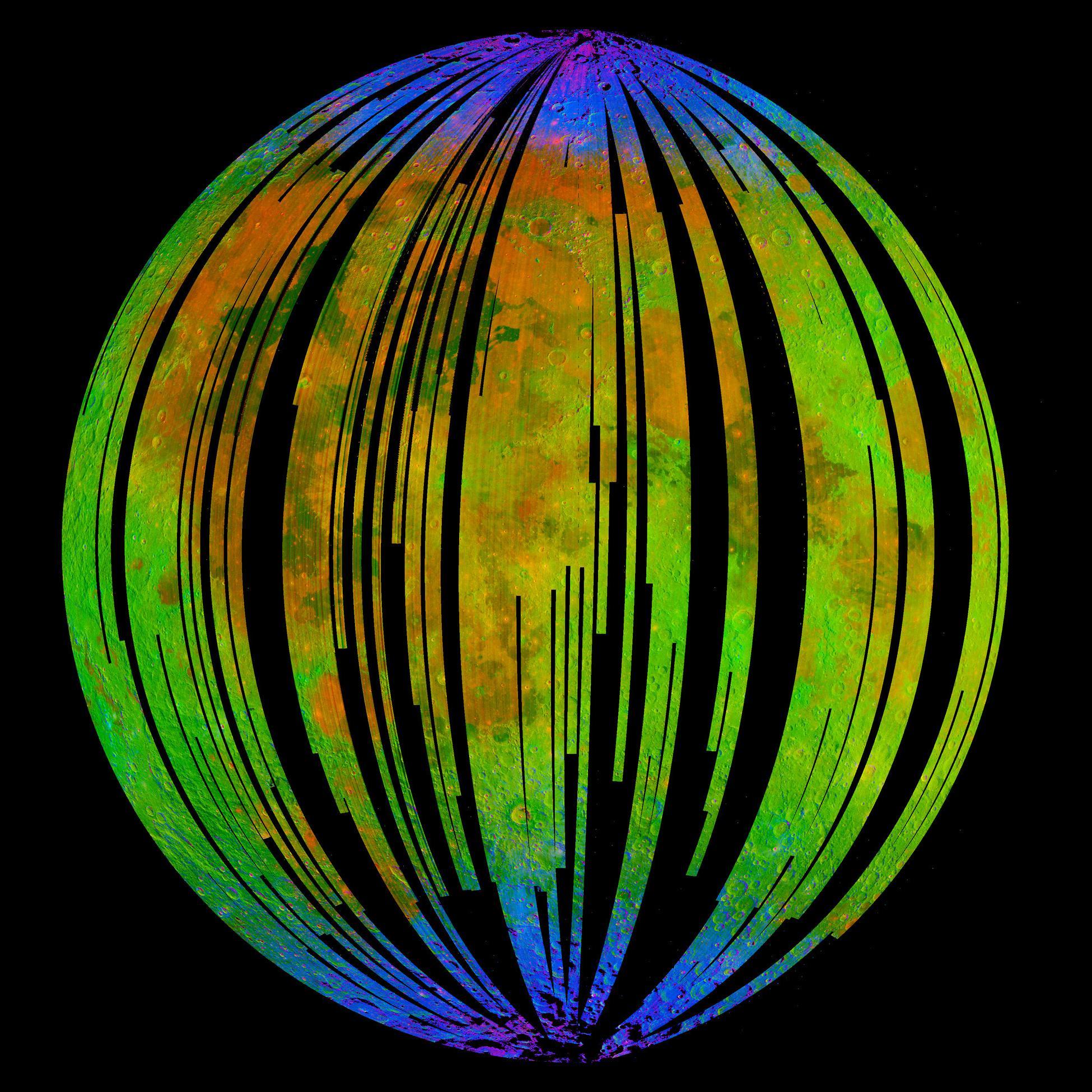
“Water detected at high latitudes on the Moon.” graphic image by NASA, 2008. Public domain image. Included with appreciation.
Back on Earth, Year of the Water Rabbit opens a holiday with a long tradition. In China, as early as the 14th century bce, astronomers began to track solar longitude and lunar phases, forming the basis for a scientific yearly cycle. In China, around the time when the Grand Canal began to take shape, the Shang Dynasty (1600-1046 bce) initiated the tradition of honoring the new year. The following Zhou Dynasty (1046-256 bce) continued the custom, now turning its purpose to wishes for a good harvest in the soon-to-come spring. But it was not until the Han Dynasty (202 bce – 220 ce) that a method for determining the date was added, and families began to plan gatherings to feast and celebrate. The ancient lunar calendar was replaced in 1912 by the common, so-called Gregorian, calendar, but by 1949, popular practice prevailed and a public holiday period was renamed “Spring Festival” but is still called by many, Lunar New Year. Across Asia, and around the world, festivities feature feasting by sharing “longevity noodles.”

Noodles are a Lunar New Year culinary tradition. “New Year Prosperity Toss,” by photographer Jayden Teo, 2020. Creative commons 4.0. Included with appreciation.
How did the Lunar New Year or Spring Festival tradition become associated with animals? The origins of the practice are shrouded in ancient history, but some folk legends exist. Naming years after animals is surely more poetic and interesting than sequential numbering. Around the first century ce, the zodiac menagerie was grafted onto a 12-year cycle repeating within a 60-year system. Within that system, animals dance through the elements of water, wood, fire, earth, and metal. Behold 2023: Year of the Water Rabbit.

Find the rabbit above. “Chinese Zodiac” by RootOfAllLight, 2018. Wikimedia Creative Commons, 4.0 Included with appreciation.
Brooke, K. Lusk and Zoë G. Quinn. “Thank you and Good Night, Jade Rabbit.” 5 August 2016. Building the World Blog, University of Massachusetts Boston. https://blogs.umb.edu/buildingtheworld/2016/08/05/thank-you-and-good-night-jade-rabbit/
Douma, M. curator. “Calendars through the Ages.” WebExhibits.org, Institute for Dynamic Educational Advancement (IDEA). https://www.webexhibits.org/calendars/calendar-chinese.html
East Asian Studies and Asian American Studies, School of Humanities. “Lunar New Year 2023.” University of California, Irvine. https://www.humanities.uci.edu/news/lunar-new-year-2023
Liu, J. et al., “Evidence of water on the lunar surface from Chang’e-5 in-situ spectra and returned samples. Nat Commun 13, 3119 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30807-5
Timothy S.Y. Lam Museum of Anthropology. “History of Chinese New Year,” Wake Forest University. https://lammuseum.wfu.edu/education/teachers/chinese-new-year/history-of-chinese-new-year/
Building the World Blog by Kathleen Lusk Brooke and Zoe G. Quinn is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Un

